Types of Maritime Simulation Training Software and Devices
What are the Different Types of Maritime Simulation Training?
Simulation is the imitation of the operation of a real-world process or system over time. The act of simulating something first requires that a model be developed; this model represents the key characteristics or behaviors/functions of the selected physical or abstract system or process. The model represents the system itself, whereas the simulation represents the operation of the system over time. Simulation is used in many contexts, such as simulation of technology for performance optimization, safety engineering, testing, training, education, and video games. Often, computer experiments are used to study simulation models. Simulation is also used with scientific modelling of natural systems or human systems to gain insight into their functioning. Simulation can be used to show the eventual real effects of alternative conditions and courses of action. Simulation is also used when the real system cannot be engaged, because it may not be accessible, or it may be dangerous or unacceptable to engage, or it is being designed but not yet built, or it may simply not exist.
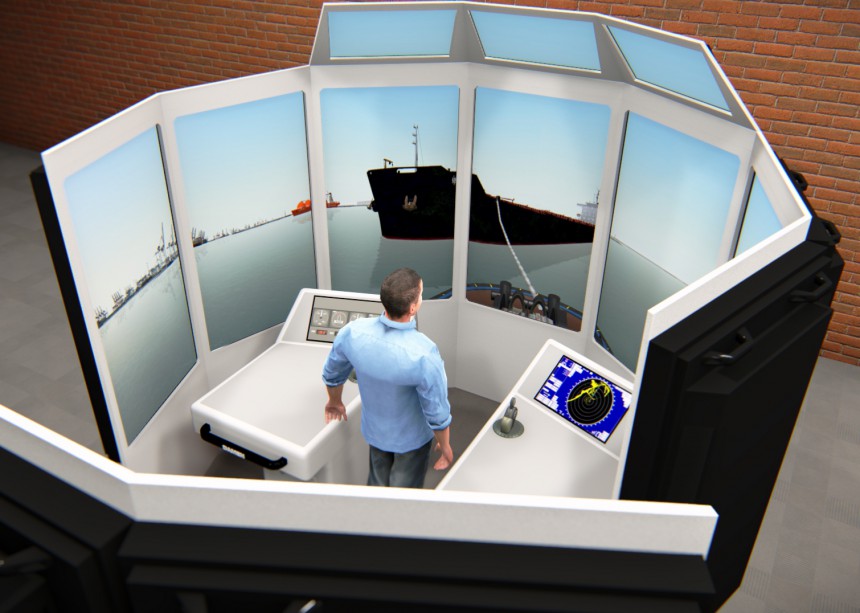
There are many different types of maritime simulation training software and devices to ensure safety and compliance training for maritime professionals. Device types range from virtual engine room simulators to ship handling simulators. Maritime training simulators bear a great deal of resemblance to flight simulators in terms of the methodologies used to train the ships’ personnel. The most common maritime simulators include:
- Ship’s bridge simulators
- Engine room simulators
- Cargo handling simulators
- Communication / GMDSS simulators
- ROV simulators
Simulators like these are mostly used within maritime colleges, training institutions and navies. They often consist of a replication of a ships’ bridge, with operating console(s), and a number of screens on which the virtual surroundings are projected. No matter the type, simulator training can be optimized for the best training experience and results when used in conjunction with a training management system (TMS) that reliably records, tracks and monitors trainee and instructor data, grades and performance in one centralized system to ensure regulatory compliance.
Spotlight on From Engine Room Simulators to GMDSS & Ship Handling Simulators
Among this wide array of maritime simulators, there are various design types of engine room training, ship handling and GMDSS simulators, which is the Global Maritime Distress and Safety System. Please reference the IMO’s GMDSS Handbook 2015 Edition for more information. Some engine room simulators can be shipped in desktop or standalone consoles, up to a complete full mission installations. The navigation simulators include steering or boat-handling stands. All simulators provide instructor software such as a TMS like AQT Solutions’ ATMS (Advanced Training Management System).
- Virtual Engine Room Simulator: Models a conventional low speed diesel engine and an electronically-controlled version of the same engine. It can be supplied as software only, in a desktop console or in a full size console.
- Turbo Diesel Simulator: Management simulator in which the user responsible for the operation and maintenance of a marine diesel engine.
- Gas Turbine Simulator: Simulates a naval engine room powered by a two-shaft gas turbine.
- Steam Engine Room Simulator: Simulates typical steam turbine operations with all auxiliary systems. Supplied as software only.
- Full Mission Simulators: Comprised of full size switchboard panels, control room consoles, sound system, communication system, PCs and networking, with locally delivered operator training.
- Steering Simulators: Designed to conform to Section A-II/4 of STCW Code for the training of ratings forming part of a navigational watch on sea-going and river vessels.
- Small Craft Simulators Train small craft navigators on a variety of small craft in both open sea areas and inland waterways, including Coast Guard personnel and Marine Patrol Inspectors.
- Survival Craft Simulator: Train seafarers designated to take charge of survival craft and rescue boats in accordance with the STCW Code.
Sources: Photo by Nautis; J. Banks, J. Carson, B. Nelson, D. Nicol (2001). Discrete-Event System Simulation. Encyclopedia of Computer Science
Discover Today’s Most Advanced
Maritime Training Management System